Advertisement
Tonsils, medically referred to as palatine tonsils, are part of a group of tonsils located in different areas of the throat. The palatine tonsils, which are the most commonly referred to, are situated in the oropharynx. If you open your mouth wide, you'll see a small uvula at the back of your throat, and on either side of it, just above the tongue, are two fleshy masses. These are the palatine tonsils. Some people might have noticed these two masses and wondered what they are—those are the palatine tonsils. There are also other types of tonsils, such as the pharyngeal tonsils and the tubal tonsils, but our focus here is on the palatine tonsils and tonsillitis that affects them.

Based on the duration of the illness, tonsillitis can be classified into acute and chronic tonsillitis.
Acute Tonsillitis
Acute tonsillitis is an acute inflammatory condition, generally caused by bacterial infections, most commonly group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, or other bacteria. It usually occurs when the body's resistance is low, leading to the onset of acute tonsillitis.
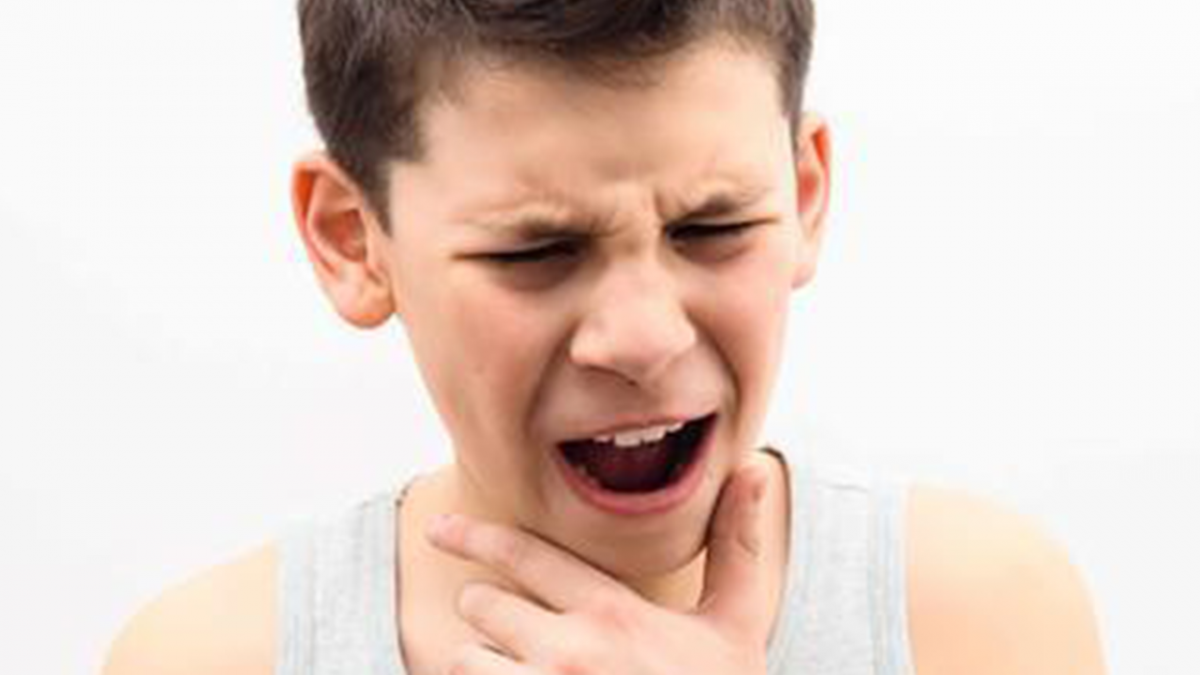
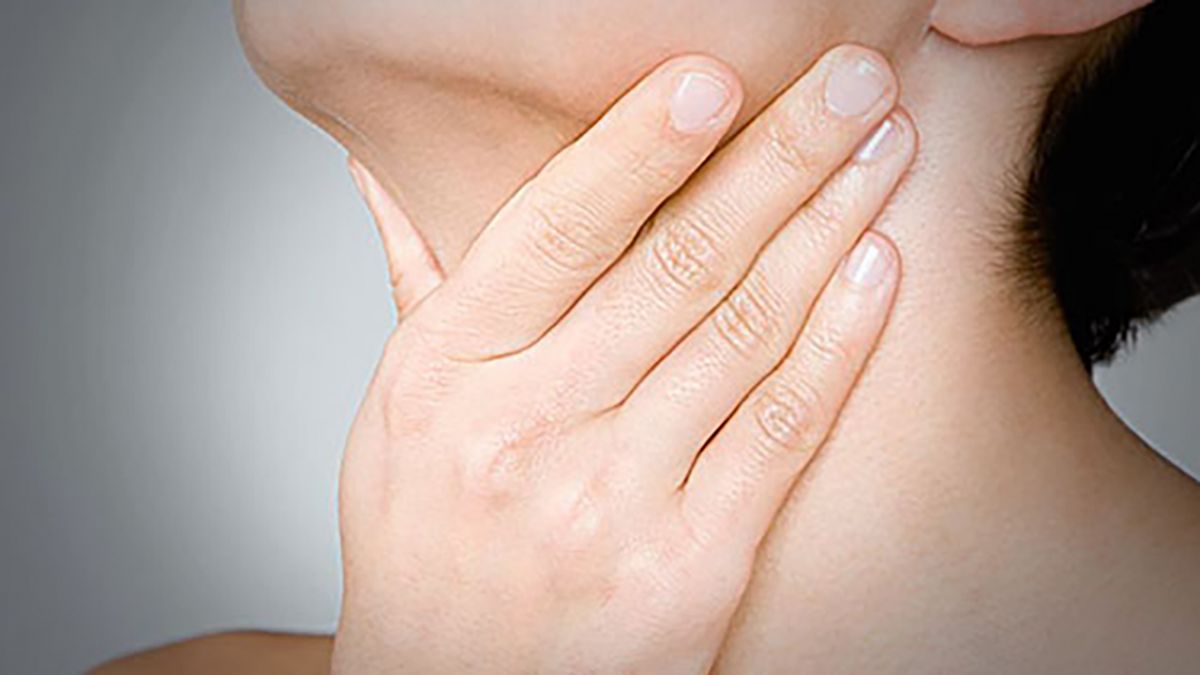
Patients with acute tonsillitis experience severe throat pain. This pain can be localized to one side of the throat or affect both sides. The pain can also radiate; aside from a sore throat, it may extend to the ears, causing ear pain. Some patients may even seek medical attention primarily for ear pain, only to find out through examination that the root cause is inflammation of the tonsils. This radiating pain is a key local symptom of the condition.
In addition to these local symptoms in the oropharynx, patients with acute tonsillitis often experience systemic symptoms. These can include high fever, chills, shivering, decreased appetite, and body aches. The systemic symptoms are usually quite pronounced, forming a significant part of the clinical presentation of acute tonsillitis.
If acute tonsillitis is not treated promptly, it can progress to chronic tonsillitis in some patients.
Chronic Tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by recurrent episodes of acute tonsillitis. Patients may experience throat pain three to four times a year, or even more frequently, with some patients having flare-ups as often as seven to eight times a year. This recurrent throat pain is a primary clinical symptom of chronic tonsillitis.

In addition to these acute episodes, patients may experience discomfort in the throat during the intervals between episodes. This discomfort can manifest as a persistent sore throat, a feeling of a foreign object in the throat, a burning sensation, itching, or even a frequent urge to cough. These symptoms are indicative of the clinical presentation of chronic tonsillitis.
Advertisement