Advertisement
Frequent nosebleeds, or epistaxis, in adults can be attributed to a range of underlying causes, each with its own implications for diagnosis and treatment. This article explores the potential reasons behind recurrent nosebleeds and outlines the typical diagnostic methods used to address the issue effectively.

Potential Causes of Frequent Nosebleeds
In adults, the causes of frequent nosebleeds can differ significantly from those observed in children. One common type of nosebleed involves sudden and substantial bleeding from a ruptured blood vessel. This type of bleeding is often dramatic and may stop temporarily with home remedies such as pinching the nostrils or applying ice. The bleeding typically originates from either the anterior (front) or posterior (back) parts of the nasal cavity and is often linked to dryness that leads to the formation of crusts or damage to the superficial blood vessels.
The underlying reasons for the fragility of these vessels can vary. Anatomical issues, such as a deviated nasal septum, can cause localized turbulence and increased negative pressure on specific areas of the nasal cavity. This results in superficial blood vessels, particularly those in the arteries, becoming more susceptible to rupture and bleeding.
Another significant factor contributing to nasal bleeding in adults is high blood pressure, or hypertension. Elevated blood pressure can lead to both intracranial (inside the skull) and extracranial (outside the skull) bleeding due to the increased stress placed on blood vessels. Managing and controlling hypertension is crucial, as uncontrolled high blood pressure can exacerbate bleeding tendencies and lead to more severe complications.
Nasal tumors are another important consideration. Tumor-related nosebleeds often present differently from other types, typically appearing as blood-streaked nasal discharge rather than sudden, severe bleeding. This type of bleeding is usually due to tumor ulceration and tends to be persistent, gradually worsening over time. Unlike bleeding caused by infections or inflammation, which often resolves within a few days, tumor-related bleeding can be chronic and requires a thorough examination. Nasal endoscopy is a critical tool in this scenario, as it allows for direct visualization of the nasal cavity to identify potential tumors.
In addition to tumors and hypertension, trauma to the nasal area is a straightforward cause of nosebleeds. This type of bleeding is often easily diagnosed based on recent injuries or accidents. However, there are also rare hereditary conditions that can lead to frequent nosebleeds. One such condition is hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), which is characterized by fragile blood vessels that are prone to bleeding. In these cases, even minor activities can trigger nosebleeds, and patients may need specialized care and treatment.
Diagnostic Approaches
When patients with frequent nosebleeds seek medical attention, several key diagnostic steps are typically undertaken to identify the cause and determine appropriate treatment:
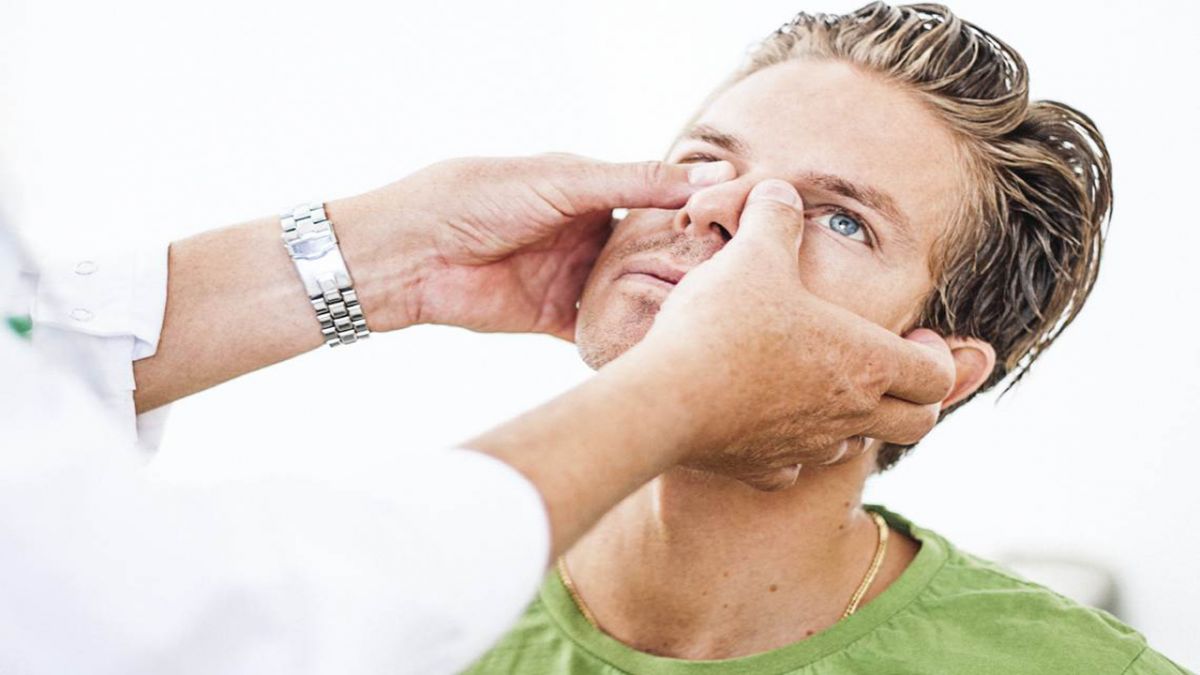
Nasal Endoscopy: The primary diagnostic tool for evaluating nosebleeds is nasal endoscopy. This procedure allows doctors to directly visualize the nasal cavity and identify the exact source of the bleeding. The simplest method is anterior rhinoscopy, which examines the front part of the nose. If anterior rhinoscopy does not reveal the bleeding source, a more comprehensive nasal endoscopy is performed to inspect the deeper and posterior areas of the nasal cavity.
Systemic Disease Evaluation: It is essential to investigate whether systemic diseases or conditions are contributing to the nasal bleeding. This involves checking for hypertension through blood pressure measurements, conducting a complete blood count (CBC), and evaluating for underlying conditions such as blood cancers, kidney failure, or liver dysfunction. These systemic conditions can impact blood coagulation and contribute to bleeding issues.
Additional Imaging and Testing: Depending on the findings from nasal endoscopy and systemic evaluations, additional imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI may be necessary to assess the extent of any tumors or other abnormalities within the nasal and sinus cavities. Blood tests to check for coagulation disorders or other systemic issues may also be performed.
In conclusion, frequent nosebleeds in adults can arise from a variety of causes, including hypertension, tumors, nasal trauma, and rare hereditary conditions. Accurate diagnosis involves identifying the precise source of bleeding through nasal endoscopy and evaluating for systemic conditions that may contribute to the problem. Effective management requires addressing both the immediate cause of the bleeding and any underlying health issues to ensure proper treatment and prevention of future episodes.
Advertisement