Advertisement
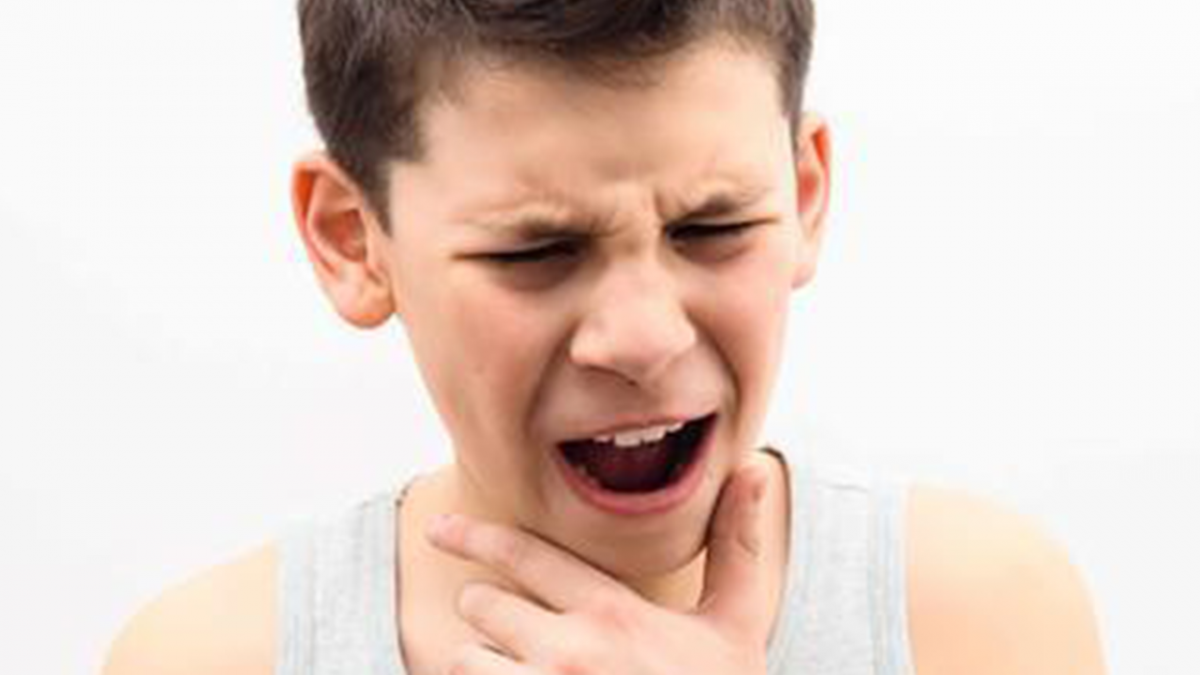
Nasal congestion, or a stuffy nose, is most commonly seen in everyday life due to colds or rhinitis. But why exactly does the nose get congested, and are there any ways to relieve it?

The primary reason is swelling. Redness, swelling, heat, and pain are the typical and classic signs of inflammation. What is redness? It's the result of congestion. While you can't see the redness inside the nasal cavity, a doctor can examine it and note nasal congestion. What is swelling? Inflammation causes fluid to seep out, leading to tissue swelling. On the body’s surface, inflammation and swelling are visible, but inside the nasal cavity, the swelling is hidden. The normal structures inside, especially the inferior turbinates, can swell significantly. When a doctor examines the nose and observes this, they might describe the inferior turbinates as hypertrophic or swollen. This swelling of the inferior turbinates causes nasal obstruction, which is one of the most common causes of nasal blockage. Other causes include purulent secretions blocking the nasal passage, which can be relieved by clearing the secretions. Nasal tumors are another cause, leading to mechanical obstruction of the nasal passages.
Why do colds or rhinitis cause nasal congestion? As we discussed, redness, swelling, heat, and pain are the hallmarks of inflammation, but pain in the nasal cavity due to colds or swelling is quite rare. Why is it rare? The tissue of the turbinates is very loose, and when it swells due to inflammation, it doesn’t compress nerve endings as tightly, so the pain is not as pronounced.
Which areas of inflammation cause the most pain? Teeth. When a person has a slight tooth infection, their primary complaint is severe pain, not swelling or secretions, which are not usually present. The tissue in the teeth is very hard, so inflammation is trapped inside, pressing tightly against nerve endings, leading to intense pain. The throat can also hurt due to inflammation, even though the tissues are loose, because it's a moving organ. Inflammation in a moving organ can compress nerve endings during certain movements, causing significant pain. This explains pain related to inflammation.
However, the primary reason for nasal congestion due to inflammation is turbinate swelling. Therefore, treatment often focuses on addressing this. One of the simplest self-care methods is to apply a warm towel to the area to promote blood circulation. A little heat can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, causing blood vessels to constrict slightly, improving nasal airflow. This is a very simple technique. Many herbal preparations also include a bit of menthol, combined with heat and steam for inhalation, which can temporarily relieve symptoms.
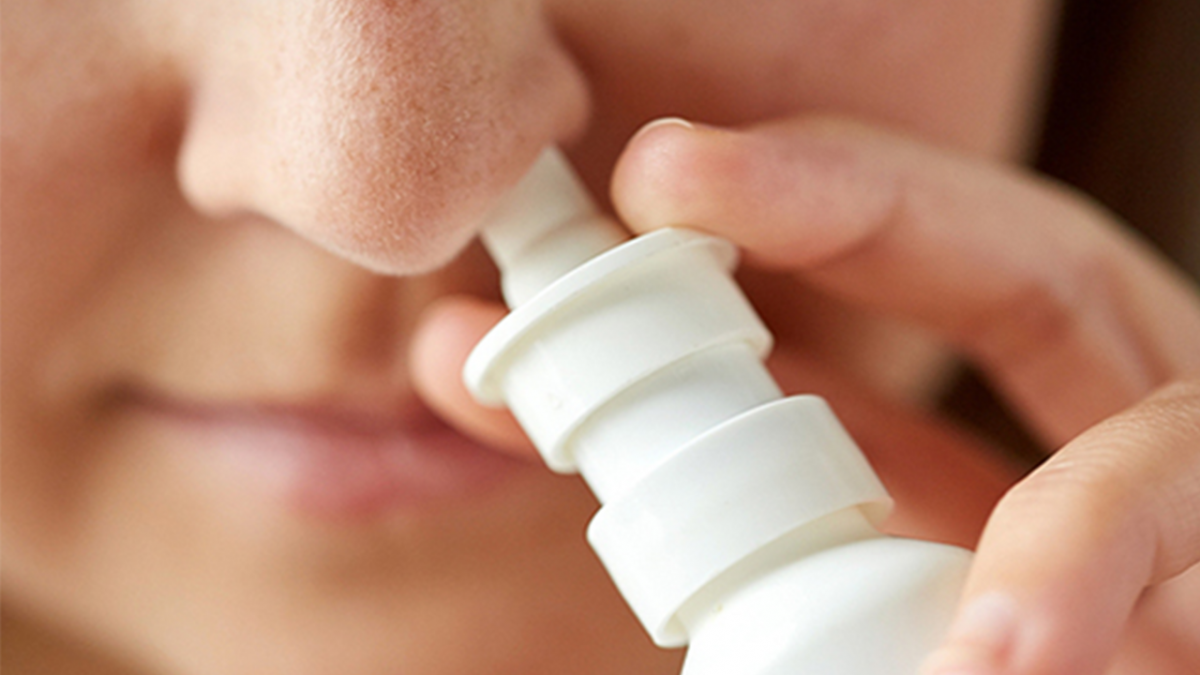

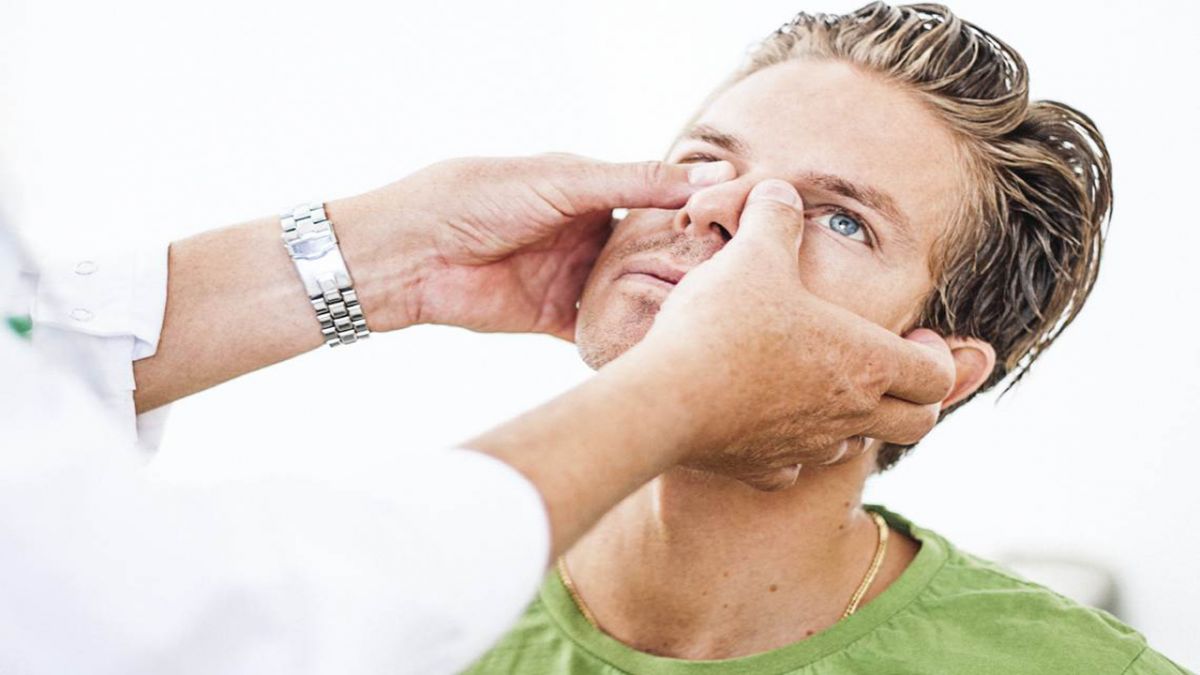
There are also saline solutions available on the market for nasal irrigation. Some saline solutions are hypertonic, which, when sprayed, have a dehydrating effect that can reduce turbinate swelling and improve airflow quickly. In the nasolabial fold area, there is a pressure point called the Yingxiang point. Pressing on this point can stimulate the sympathetic nerves inside the nasal cavity, providing temporary relief from nasal congestion. Acupuncture can also significantly help relieve nasal congestion.
In traditional Chinese medicine, there are many remedies that can temporarily alleviate nasal congestion. Aside from these methods, sometimes medication is necessary. Doctors may prescribe vasoconstrictor drugs to patients for short-term relief; as the blood vessels constrict, the nose will quickly clear up. However, these medications should only be used under medical supervision and not for long periods, as they can cause tolerance and rebound effects. Once the medication's effect wears off, the nasal congestion can become worse than before. Over time, this can lead to drug-induced rhinitis, which is difficult to treat. Therefore, medication should be administered with caution and under the guidance of a doctor. Lastly, it's important to address the root cause of turbinate swelling, which also requires medical assistance.
Advertisement