Advertisement
Otitis externa is an inflammation of the external ear canal, which is the passage that leads from the outer ear to the eardrum. This condition can affect people of all ages and is characterized by various symptoms that can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.

There are multiple factors that contribute to the development of otitis externa. One of the most common causes is excessive moisture in the ear canal. After swimming, especially in contaminated water, water can remain trapped in the ear. This trapped water disrupts the normal dry environment of the ear canal. The warm, moist conditions are highly conducive to the growth of bacteria and fungi. For instance, Pseudomonas aeruginosa thrives in such wet environments. It can rapidly multiply, leading to an infection. Staphylococcus aureus is another common culprit. Excessive earwax (cerumen) also has a role. When earwax accumulates, it can block the normal drainage of the ear canal. This blockage traps moisture, creating a perfect environment for microorganisms to flourish. Moreover, certain skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or eczema that affect the ear canal can also predispose individuals to otitis externa as they disrupt the skin's natural barrier.
Another significant cause is mechanical trauma to the ear canal. Many people use cotton swabs, hairpins, or other small objects to clean their ears. However, these actions can scratch the delicate skin of the ear canal. Even a minor scratch can break the skin's integrity, allowing bacteria or fungi to enter and cause an infection. Allergic reactions are also a trigger. Some individuals are allergic to the materials in earplugs, such as latex. The use of certain types of earrings can also cause allergic reactions in the ear canal if the metals leach into the skin. Additionally, hair products like hairspray or shampoo that come into contact with the ear can trigger an allergic response in sensitive individuals.
The symptoms of otitis externa can vary in severity. Ear pain is one of the most prominent symptoms. It can start as a dull ache, gradually intensifying to a sharp, throbbing sensation. In severe cases, the pain can be so intense that it disrupts sleep, making it difficult for patients to get a good night's rest. It can also interfere with daily activities like chewing or talking. The ear canal often becomes itchy, which is extremely uncomfortable. Patients have a strong urge to scratch, but this only exacerbates the problem, further irritating the inflamed tissue.
The presence of discharge from the ear is another common symptom. The discharge can be clear in the early stages or when the inflammation is mild. As the infection progresses, it can turn yellow, and in cases of a more severe bacterial or fungal infection, it may become greenish - brown. This discharge often has an unpleasant odor. As the inflammation worsens, the ear canal swells. This swelling can cause a feeling of fullness in the ear. The blockage due to swelling can also lead to a temporary hearing loss. In more severe cases, the lymph nodes near the ear, such as the pre - auricular and post - auricular lymph nodes, may become enlarged and tender as the body's immune system tries to fight the infection.
Diagnosing otitis externa typically begins with a physical examination by a healthcare provider, usually an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. The doctor will use an otoscope to closely examine the ear canal. This instrument provides a clear view of the ear canal and eardrum. In cases of otitis externa, the doctor will observe redness, swelling, and the presence of discharge. If an allergic reaction is suspected, the doctor will ask about recent exposure to potential allergens like new hair products, earplugs, or changes in earrings.
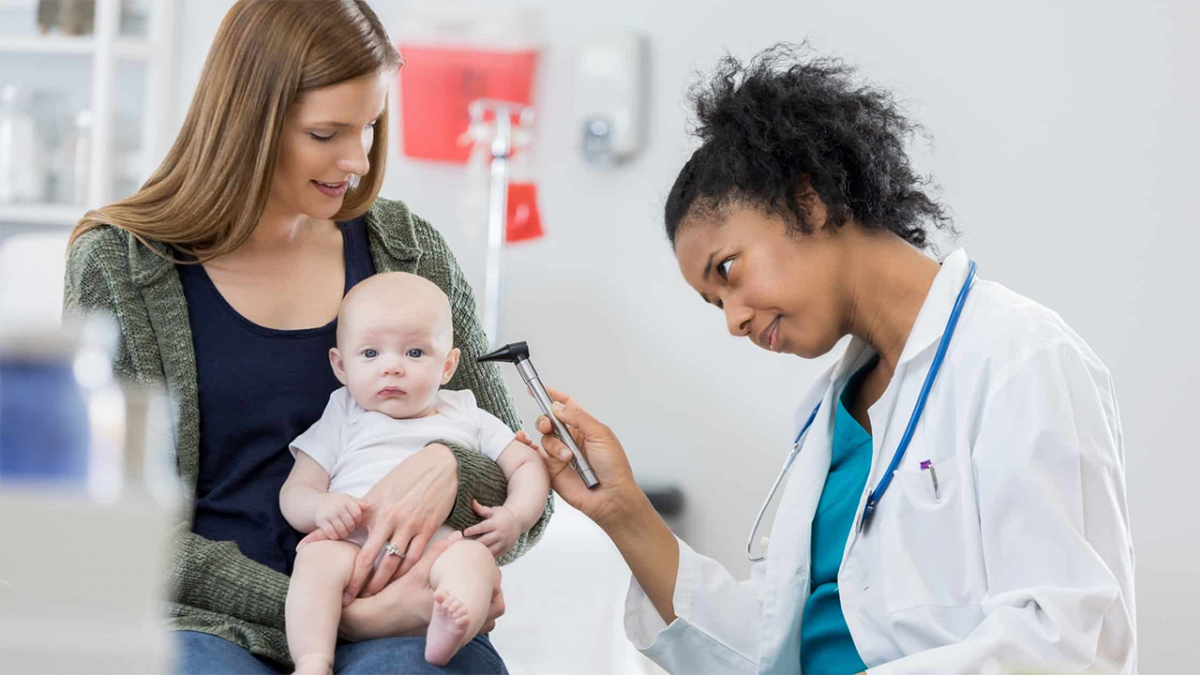

In some cases, further testing is required. A swab of the ear canal may be taken to identify the specific bacteria or fungus causing the infection. This information is crucial for determining the most appropriate antibiotic or antifungal treatment. If the hearing loss is significant, audiometric testing may be ordered to accurately assess the extent of the hearing impairment.
Treatment for otitis externa depends on the severity and cause of the condition. For mild cases, keeping the ear dry is essential. A hair dryer on a low - heat setting can be used to gently dry the ear canal after swimming or bathing. Over - the - counter ear drops containing acetic acid can help restore the normal acidic environment of the ear canal, inhibiting bacterial growth.
In cases of bacterial infection, prescription antibiotic ear drops like ofloxacin or ciprofloxacin are commonly prescribed. If the infection is severe or has spread to the surrounding tissues, oral antibiotics may be necessary. For fungal infections, antifungal ear drops such as clotrimazole are used.
If the cause is an allergic reaction, avoiding the allergen is the first step. Antihistamines may be prescribed to reduce the allergic response, and corticosteroid ear drops can be used to decrease inflammation.
In conclusion, otitis externa is a common ear condition that can cause significant discomfort. Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking prompt medical treatment can help in effectively managing the condition and preventing potential complications.
Advertisement